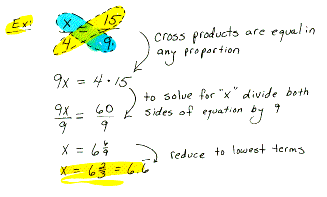Mathematical
"S" Words
Mathematical
"S" Words
*Dictionary
Alert
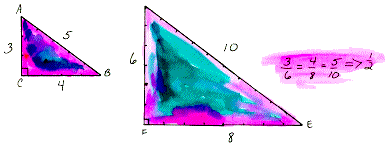
scale factor of size transformation In similar figures, the ratio of a distance or length in an image to the corresponding distance or length in a preimage. Also called ratio of similitude.
Ex: When comparing the following small right triangle to its similar large right triangle, we see a scale factor of 1/2 or 0.5.
scalene
triangle
A triangle with no two sides of the same length.
scientific calculator A calculator which writes very large or small numbers in scientific notation and uses the powering, factorial, square root, negative, and reciprocal keys. This type of calculator has the proper arithmetical, "order of operations" installed in its brain. So it knows that parentheses must be calculated first, then exponents, then multiplication and division from left to right, and finally addition and subtraction from left to right.
*Remember a cheap, non scientific calculator will perform the operations in the order that you enter them, so if you type 3+2x4 on a non scientific calculator, you get 20, which is the WRONG answer. The multiplication needs to be done FIRST so the correct answer is 11. A scientific calculator will give you the correct answer, because it knows it must multiply FIRST.
scientific notation for large numbers A way of writing a large number in terms of a positive integer power of 10 multiplied by a number greater than or equal to 1 and less than 10.
Ex:
scientific notation for small numbers A way of writing a small number in terms of a negative integer power of 10 multiplied by a number greater than or equal to one and less than 10.
Ex:
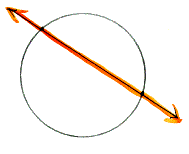
secant to
a circle A
line that intersects a circle in two distinct points.
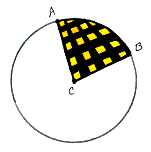
sector of
a circle
The figure bounded by two radii and the included arc of the circle.
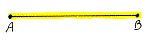
segment
On a line, the set consisting of the distinct points A and B (its endpoints)
and all points between A and B. Also called line segment.
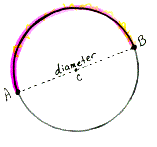
semicircle Half a circle. The arc of a circle whose endpoints are the endpoints of a diameter of the circle.
Ex:
is a semicircle of circle C.
short ton A unit of weight in the U.S. system of measurement equal to 2,000 pounds.
side One of the segments which makes up a polygon. One of the rays of an angle. One of the faces of a solid.
side of
an angle An
angle is the union of two rays with the same endpoint.
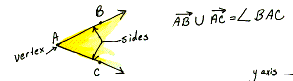
The rays are the sides and the common endpoint is called the vertex.
There are many types of angles. See the definitions for zero angle, right
angle, straight angle, acute angle, obtuse angle and reflex angle.
side of a polygon One of the segments whose union is a polygon; also, the length of that segment.
similar figures Two figures that have the same shape, but not necessarily the same size.
simple closed curve A figure that is closed and does not intersect itself.
simple fraction A fraction with an integer in the numerator and a nonzero integer in the denominator.
sine of an angle The ratio (leg opposite the angle / hypotenuse) in a right triangle. Abbreviated sin.
size
change factor
A number which multiplies other numbers to a change their size.
Ex: |
Here we see a size change factor of 1/2 going from the large triangle to the small. Or a size change factor of 2 if going from the small to the large triangle.
size change of magnitude k A transformation in which the coordinates of the original figure have all been multiplied by k. Also called size change factor, and ratio of similitude.
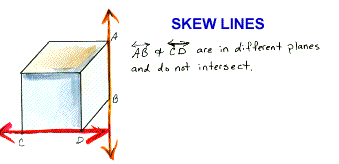
skew lines
Lines
that do not lie in the same plane and do not intersect.
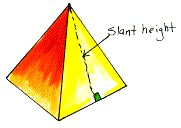
slant
height of a regular pyramid The altitude from the vertex on
any one of the triangular, lateral faces of the pyramid. It is important
to remember that the slant height is not the acutal height of the pyramid
itself; it is just the height of one of the triangles that form a
face of the pyramid.
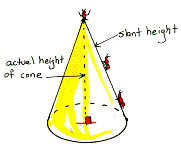
slant
height of a right cone The length of a lateral edge of the
cone. It is important to note that the slant height of a right cone
is not the height of the cone itself; it is just the distance a bug
would walk if he walked in a straight line from a point on the base directly
up to the vertex of the cone.
slide
A translation of a given preimage. This occurs when given numbers are
added to every "x" coordinate and or "y" coordinate
of the preimage. The result is that the image appears to "slide"
away from the preimage.
slide image The result of adding the same number to the coordinates of the point in a figure. Also called translation image.
slope
The name for the constant rate of change between two points on a line.
The amount of change in the height of the line as you go one unit to the
right. The slope of the line through (x1,y1)
and (x2,y2) is
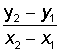 ................SLOPE
IS ALSO DESCRIBED AS:
................SLOPE
IS ALSO DESCRIBED AS:
![]() .
.
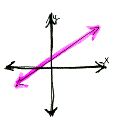
A line with a positive slope
will rise uphill from left to right.
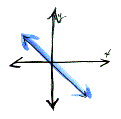
A line with a negative slope
will fall downhill from left to right.
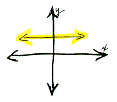
A line with zero slope
is horizontal because it has no rise between any two points.
A vertical line has undefined
slope because between any two points there is no run.
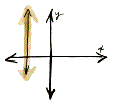
slope-intercept form An equation of a line in the form y=mx+b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
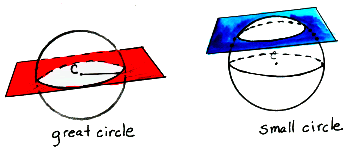
small
circle of a sphere The intersection of the sphere and a plane
that does not contain the center of the sphere.
solid
The union of a surface and the region of space enclosed by the surface.
solid geometry The study of figures in three-dimensional space.
solution A value of a variable that makes an open sentence true.
Ex: Given 3x+4=10, ............x=2 is the solution.
solving an open sentence Finding value(s) of the unknown(s) in an open sentence that make it true.
solving a proportion Finding the value of a variable that makes a proportion true.
space The set of all points in a geometry.
space figure A figure whose points do not all lie in a single plane. Also called a three-dimensional figure.
special case An instance of a pattern used for some definite purpose.
Ex: Given the inequality
, x=0 is a special case. In fact this special case proves that the given statement is false, because
would be 0, and 0 is not greater than zero. Thus this special case is a counterexample to the given statement.
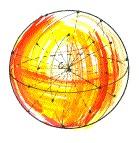
sphere The set of points in space at a fixed distance (its radius) from a point (its center).
*Note this definition implies that all of the points on the iterior, or at a distance less than the radius, are not part of the sphere. If you want all those points too, you need something called a spherical solid.
square A four-sided figure with four right angles and four sides of equal length. A rectangle with the same length and width.
square root If A = s^2 , then s is called a square root of A.
Ex:
since both 3 and -3 are 9 when squared. Remember there are always two possible square roots, one positive, called the "principal" square root, and one negative.
square units Units for measuring area.
Ex: square inches, square meters, square miles, etc..
standard form of an equation for a line A equation for a line in the form Ax+By=C, where A and B are not both zero.
straight angle An angle whose measure is 180°.
straightedge An instrument for drawing the line through two points which has no marks for determining length.
Substitution Principle If two numbers are equal, then one may be substituted for the other in any computation without changing the results of the computation.
subtrahend b in the subtraction a - b.
sufficient condition p is a sufficient condition for q if and only if p implies q.
sum The result of an addition.
supplementary angles Two angles whose measures add to 180°.
surface The boundary of a three-dimensional figure.
surface area The sum of the areas of the faces of a solid.
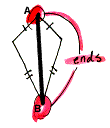
symmetry
diagonal (of a kite) The
diagonal that connects the ends of the kite.
symmetric
figure
A figure that coincides with its reflection image over a line.
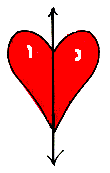
symmetry line For a figure, a line m such that the figure coincides with its reflection image over m. See above the heart figure with the symmetry line down its center.
symmetry
plane
For a figure, a plane M such that the figure coincides with its reflection
image over M.
synthetic geometry A geometry studied without the use of coordinates.
Home | About
Us | Algebra| Dictionary | Games | Geometry | Gym | Humor | Lab | Magic | Natural Math | PreAlgebra | Resources | Teachers Only | Toolbox | Treasures | Videos | Wonders | Writings |
Copyright © 1999-2020 themathlab.com